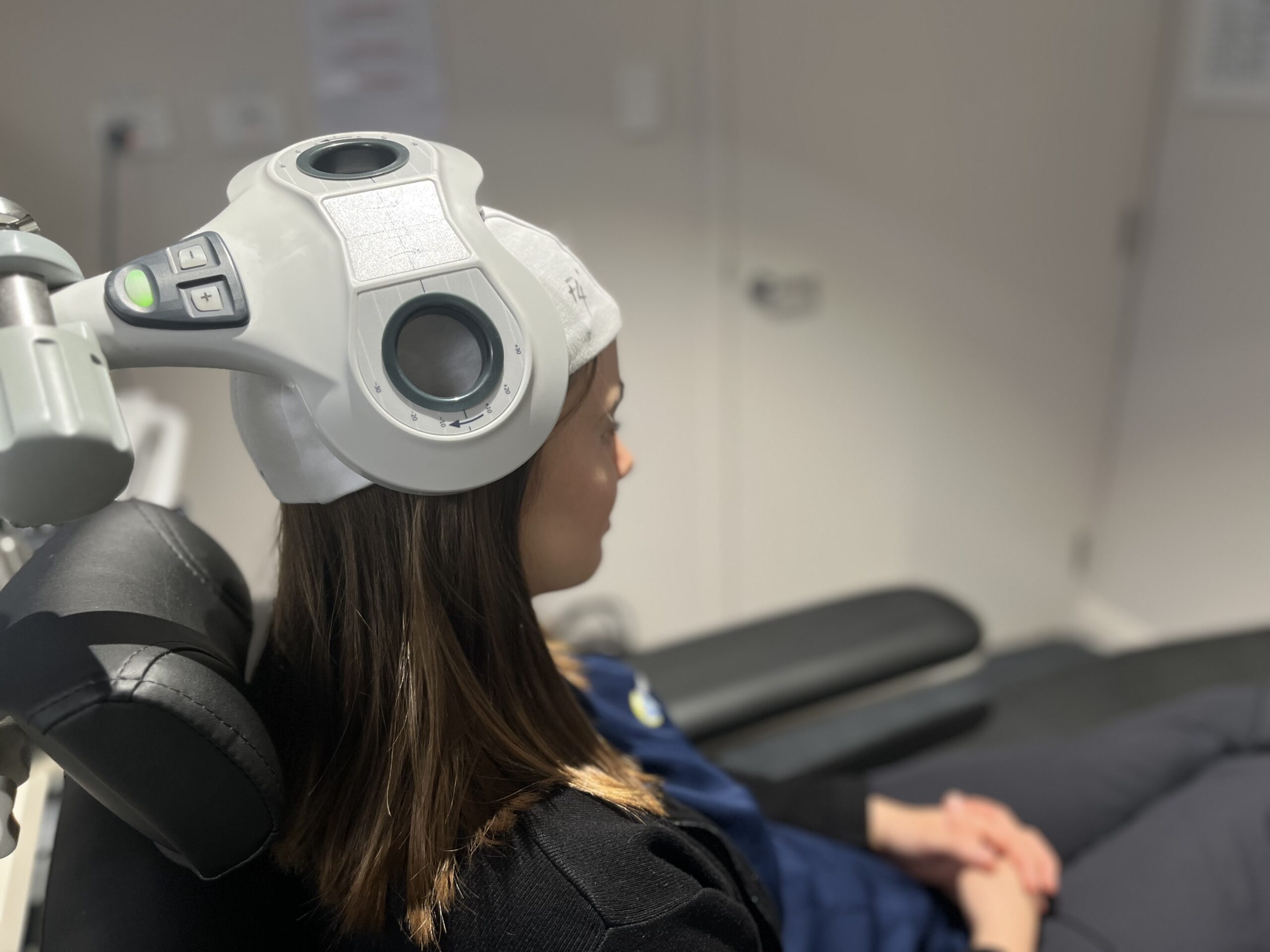
Health Professionals
As a health professional, integrating TMS into your patient’s treatment can offer a therapeutic option for patients suffering from treatment-resistant depression, anxiety disorders, certain chronic pain syndromes, plus a number of other conditions. With its proven efficacy and an excellent safety profile, TMS has garnered increasing attention as an alternative or adjunct to traditional therapies. The following table summarises the efficacy of TMS for a variety of conditions. You can read the full article that this information is extracted from here.
Evidence for TMS (Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation)
|
|
|
|---|---|
|
Depression
|
Definite antidepressant efficacy in major depression (Level A)
|
|
Post-traumatic stress disorder
|
Probable efficacy in PTSD (Level B)
|
|
Obsessive compulsive disorder
|
Possible efficacy in OCD (Level C)
|
|
Neuropathic pain
|
Definite analgesic efficacy to pain side (Level A)
|
|
Migraine
|
FDA approved TMS devices for the treatment of migraine.
|
|
Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS) type I
|
Possible analgesic efficacy to pain side (Level C)
|
|
Fibromyalgia
|
Probable efficacy in improving quality of life of patients with fibromyalgia (Level B) Probable analgesic efficacy in patients with fibromyalgia (Level B)
|
|
Parkinson’s disease
|
Probable efficacy in motor symptoms of PD patients (Level B)Probable antidepressant efficacy in PD patients (Level B)
|
|
Tinnitus
|
Possible efficacy in chronic tinnitus (Level C)
|
|
Schizophrenia: auditory hallucinations
|
Possible efficacy in auditory hallucinations in schizophrenia (Level C)
|
|
Schizophrenia: negative symptoms
|
Possible efficacy on negative symptoms of schizophrenia (Level C)
|
|
Motor stroke
|
Definite efficacy in hand motor recovery at the postacute stage (Level A)
|
|
Post-stroke aphasia
|
Probable efficacy in nonfluent aphasia recovery at the chronic stage (Level B)
|
|
Multiple sclerosis
|
Probable efficacy to the most affected limb in lower limb spasticity (Level B)
|
|
Alzheimer’s disease
|
Possible efficacy to improve cognitive function, memory and language level of AD patients, especially at a mild/early stage of the disease (Level C)
|
Clinical Neurophysiology | Volume 131, Issue 2, February 2020, Pages 474-528
TMS Referrals
How to refer a patient for TMS
We accept referrals from GPs, psychiatrists or other health professionals.
Please submit the form relevant to your patient’s condition.
Alternatively, patients can contact us directly to arrange a referral.
For treatment resistant depression
To be eligible for Medicare covered treatment, patients must have tried antidepressants from two different classes with no success (either due to inadequate responses or intolerable side-effects).





Referral Form - TMS for Depression (Treatment Resistant)
For all other conditions
Including chronic pain, PTSD and depression for those not eligible for Medicare rebate.



